Menstrual cycles naturally fluctuate, but noticeable changes, like heavier bleeding or an irregular rhythm, can still feel unsettling. While you can help ease some symptoms through lifestyle changes and supplements like FLO PMS vitamins, understanding what drives these shifts can help you recognize what’s normal and what may be worth discussing with a healthcare professional.
A combination of daily habits, hormonal fluctuations, and underlying health conditions can all impact how a cycle behaves. Learning how these elements interact can offer clarity and help you better understand what your body may be trying to tell you.
What Constitutes a Heavy or Irregular Period?
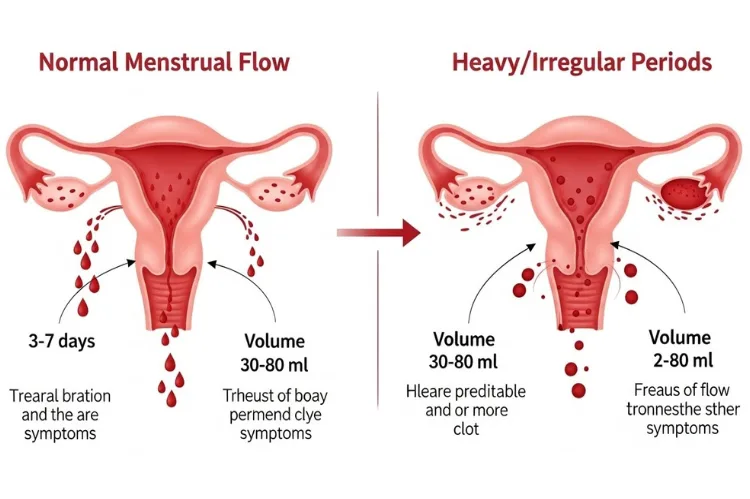
A heavy period generally involves bleeding that lasts longer than your usual cycle, requires frequent pad or tampon changes, or includes larger-than-normal clots. An irregular period may come earlier or later than expected, extend longer than a typical cycle, or skip an entire month. Because menstrual cycles involve a complicated interaction of hormones, variations in flow and timing can happen occasionally without indicating a problem.
However, when changes become persistent or disruptive, they should be taken seriously. A person who normally experiences predictable cycles might feel alarmed when bleeding patterns shift suddenly, but understanding the body’s mechanisms helps reduce anxiety.
Fluctuations often occur due to stress, hormonal adjustments, lifestyle changes, or temporary health disruptions. Recognizing what qualifies as genuinely heavy or irregular is the first step in determining whether further evaluation is necessary.
What Common Factors Influence Menstrual Changes?
Stress is one of the most common causes of cycle changes. Emotional stress, work pressure, travel, major life adjustments, or sleep disruption can influence hormone production. When stress levels rise, the brain may temporarily alter the signals sent to the ovaries, causing early, late, or missed periods. Once stress decreases, cycles often return to normal.
Lifestyle habits also contribute to irregularities. Significant changes in weight, restrictive eating patterns, or sudden increases in physical activity can affect hormonal balance. A body adjusting to rapid changes in muscle mass, body fat, or daily movement may alter menstrual timing until it reaches equilibrium. Alcohol intake, smoking, and inconsistent sleep patterns can also cause short-term fluctuations.
Age-related factors also commonly influence cycle patterns. Adolescents may experience irregular cycles for several years as their hormones regulate. People approaching their mid-40s may notice heavier bleeding, skipped periods, or cycles that arrive closer together. These changes are associated with natural hormonal fluctuations that occur during the body’s transition to menopause.
Medical Conditions That May Contribute to Changes

Some medical conditions can cause heavy or irregular periods, which makes awareness important for long-term health. Thyroid imbalances are a frequent cause, as both underactive and overactive thyroid function can disrupt menstrual regularity. Because the thyroid regulates metabolism, its influence extends to hormone production and overall cycle consistency.
Hormonal conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can also create irregular patterns. This condition often involves elevated androgen levels, which can affect ovulation and result in less predictable cycles. Individuals with this condition may experience prolonged gaps between menstrual periods or unusually long cycles.
Fibroids are another consideration. These noncancerous growths inside the uterus can lead to heavy bleeding, prolonged periods, or discomfort. They vary in size and quantity, which means symptoms can range widely. Although fibroids are common, any sudden change in bleeding should still be evaluated.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Professional evaluation is crucial when symptoms significantly interfere with daily life, cause persistent discomfort, or persist for multiple cycles. Heavy bleeding that requires changing pads or tampons every one to two hours should not be ignored. Bleeding that lasts longer than a week, occurs between periods, or includes large clots may also warrant attention.
Changes accompanied by severe cramping, fatigue, dizziness, or shortness of breath should be evaluated. These symptoms can indicate low iron levels or other conditions that benefit from timely care. Irregular cycles that persist for more than a few months may signal a hormonal imbalance or other underlying issue.
Those trying to conceive may also benefit from evaluation if irregularities become a frequent occurrence.
Understanding ovulation patterns is important, and irregular cycles can make it more difficult to predict fertile windows. A medical professional can provide guidance on how to track ovulation more accurately or determine whether treatment may help regulate cycles.
Take Control of Your Cycle
Changes in menstrual flow or timing can be concerning, but understanding the potential causes can offer clarity and confidence. Stress, lifestyle adjustments, hormonal shifts, and medical conditions all play roles in how cycles behave. Recognizing what qualifies as heavy or irregular helps determine when a medical evaluation is needed.
By paying attention to consistent patterns and seeking guidance when necessary, individuals can better support their reproductive health and their peace of mind.
Read Next: Healthy Brain Tips for Maintaining Brain Health as You Age
Jessica Fuqua is a mom of two who writes about the messy, beautiful reality of raising kids. She believes parenting advice should feel like a conversation with a friend, not a lecture. When she’s not writing, she’s probably reheating the same cup of coffee for the third time.

